Acid Base & Salt - Class 10th Science
Acids ,Bases and salt chapter :- 1 chemistry.
What is an Acid?
Taste of foods makes our life tasty. Every food we eat has some taste. Those tastes are sour, sweet or salty. Some food items have bitter taste because of base present in them. Cold drinks taste slightly bitter because of presence of base in them.
Foods give these tastes because of presence of acid, salt, sweet or base in them.
Acids
Acids are sour in taste. Food items having acids are sour in taste.
Example:
Lemon, curd, tamarind, curd, unripe fruits etc. are some most common food items that are used in households. As these items contain acids, hence these are sour in taste.
Chemical substances that are detected commonly by their sour taste are called ACIDS.
Types of Acids:
On the basis of occurrence Acid can be divided into two types: these are Natural acid and Mineral acid
Natural Acid or Organic Acid:
Acids that are obtained from natural sources such as plants, animal etc. are called natural acids. Natural acids are also called Organic Acids.
Example:
Citric acid, acetic acid, lactic acid, tartaric acid, oxalic acid, formic acid, etc.
Sources of some of the natural acids:
Citric acid: Found in lemon, orange, and in most of the citrus fruits.
Acetic acid (Ethanoic acid): Found in vinegar.
Tartaric acid: Found in Tamarind
Oxalic acid: Found in tomato
Lactic acid: Found in sour milk, curd, etc.
Formic acid: Found in ant sting, nettle sting
Ascorbic acid: Found in guava, amla, etc.
Mineral Acids or Synthetic Acids:
Acids that are prepared from minerals are known as mineral acid.
Example: Hydrochloric acid, Sulphuric acid and Nitric acid are the most common mineral acids.
As mineral acids are prepared in laboratories thus, mineral acids are also known as man-made or synthetic acids or inorganic acids.
Strong and Weak Acids:
Acid can be strong or weak.
Strong acids:
All mineral acids are strong acids except carbonic acid. For example: sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid.
Weak acids:
All organic acids i.e. naturally occurring acids are weak acids. For example: tartaric acid, oxalic acid, formic acid, acetic acid, etc.
Concentrated and Dilute Acid
Concentrated Acid:
Aqueous solution in which volume of constituents of acid is maximum is called caoncentrated acid.
Concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture.
Concentration of acid decreases with decrease the volume of constituents of acid in its aqueous solution.
Dilute Acid:
Aqueous solution of acid in which volume of constituents is not maximum is called dilute acid.
Dilution of acid increases with increase in solvent.
How to dilute an acid?
Acid can be diluted by mixing of acid into water. Dilution of acid is an exothermic process.
Caution: Always acid is slowly mixed in water to dilute the acid. Never mix water into acid to dilute. Mixing of water into acid can be very dangerous.
Properties of Acids:
- Acid tastes sour.
- Acid turns blue litmus to red.
- Dilution of acid is exothermic.
- Acids are good conductor of electricity in the solution.
- Acid forms hydrogen gas when reacts with metal.
- Acid forms salt and water when reacts with base.
Indicators
Acid and Base in Laboratory
In laboratory acid and base are detected using indicators.
Indicators
Indicators are substances which tell us that whether a given substance is an acid or a base.
Types of Indicators:
On the basis of occurrence indicators are categorized into two types:
- Natural Indicators
- Synthetic Indicators
Natural Indicators:
Indicators which are obtained naturally are called natural indicators, for example: Litmus, red cabbage, turmeric, onion, vanilla, clove, etc.
Litmus:
Litmus is a natural indicator. Litmus is soluble in water. Litmus is a type of dye and extracted from an organism called Lichen. Lichens are composite organism fungus and generally green alga, which shows symbiotic relationship.
Litmus papers are prepared by dipping filter paper into the extract of litmus. The original color of litmus is purple generally called red.
In laboratories litmus papers are frequently used to detect the acid or base.
Litmus papers come into two colours: Blue and Red.
Acid turns blue litmus paper into red.
Base turns red litmus paper blue.
Turmeric:
Turmeric is another natural indicator. The colour of turmeric is yellow.
Acid has no effect on the colour of turmeric. This means acid does not change the color of turmeric.
Base changes yellow color of turmeric to reddish brown or can be called orange.
You will notice that cloth with stain of curry turns reddish brown or orange after applying of soap when taken for washing. This happens because soaps are made of bases (Sodium bicarbonate), this base turns stains of curry, which is actually turmeric on clothes from yellow to reddish brown. This reddish brown color again turns yellow when clothes are dried.
Turmeric papers can also be made by dipping and drying the blotting, filter or toilet paper in the solution of turmeric. Turmeric solution can be made by using water.
Red Cabbage:
The juice of red cabbage is used as another natural indicator. Red cabbage is of purple color and consequently juice is purple in color.
When red cabbages grown on acidic soil, their leaves are reddish but while grown on alkaline soil, their leaves are of yellowing green color.
That’s why juice of leaves of red cabbage is used as natural indicator.
Red cabbage juice is originally purple in colour.
This juice turns reddish when acid is added.
Juice of red cabbage runs greenish when base is added.
Thus, juice of red cabbage is used as natural indicator to detect acid or base.
Olfactory Indicators:
Nature gives us many substances which change their order with acid and base. Vanilla, cloves, onion, etc. are such substances. In other words, substances which change their order with acid and base are called olfactory indicators.
Generally vanilla, cloves and onion are used as olfactory indicators to detect acid or base. Olfactory indicators are useful for visually impaired people. Use of olfactory indicators insures the participation of visually impaired students in lab activities equally.
Onion:
Onion does not lose its smell when acid is added to it.
But, onion loses its smell when base is added to it.
Keeping this character of onion, it is used as olfactory indicator.
Vanilla:
When base is added, vanilla loses its smell.
But, when acid is added, vanilla does not lose its smell.
Clove:
The smell of clove oil vanishes with base.
But, clove does not lose its smell with acid.
Synthetic Indicators:
Indicators which are made in laboratories are called synthetic indicators.
Phenolphthalein and methyl orange are two most common synthetic indicators used in laboratory.
Phenolphthalein:
Phenolphthalein is colourless solution in original.
Solution of phenolphthalein turns pink with basic solution.
But, phenolphthalein solution remains colourless with acedic solution.
Methyl Orange:
Methyl orange is an orange liquid.
Methyl orange turns yellow with basic solution.
While methyl orange turns red with acidic solution.
Chemical Properties
How do Acids and Bases React with Metals?
Acids and bases give hydrogen gas and respective salt when reacts with most of the metals. General reaction for acid and base with metals can be depicted as follows:
Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen
Base + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen
Some metals do not react with acid and base.
Examples:
Reactions of acid with metals
(1) When zinc metal reacts with hydrochloric acid, zinc chloride (a salt) and hydrogen gas are formed.
(2) When zinc metal reacts with sulphuric acid, zinc sulphate (a salt) and hydrogen gas are formed.
(3) When sodium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride and hydrogen gas are formed.
(4) When iron metal reacts with hydrochloric acid solution of iron chloride and hydrogen gas is formed.
Reaction of base with metals
(1) When sodium hydroxide reacts with zinc metal, it produces sodium zincate and hydrogen gas.
(2) When sodium hydroxide reacts with aluminium, it produces hydrogen gas and sodium aluminate.
Since, alkalis react with metals, so alkalis are not stored in metal containers.
Chemical Properties-2
How do metal carbonates and Metal Hydrogen carbonates react with Acids?
When acid reacts with metal carbonate or metal hydrogen carbonate, corresponding salt, carbon dioxide gas and water are formed.
Metal Carbonate + Acid → Salt + Carbon dioxide + Water
Metal Hydrogen Carbonate + Acid → Salt + Carbon dioxide + Water
Example:
Reaction of acids with metal carbonate:
When sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride is formed along with carbon dioxide and water.
When sodium carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid, sodium sulphate, carbona dioxide and water are formed.
When magnesium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, magnesium chloride, carbon dioxide and water are formed.
When calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, calcium chloride, carbon dioxide and water are formed.
When calcium carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid, calcium sulphate, carbon dioxide and water are formed.
When sodium carbonate reacts with nitric acid, sodium nitrate, water and carbon dioxide are formed.
Chemical Properties-3
Reaction of acid with hydrogen carbonates (hydrogen carbonates are also known as bicarbonates):
Examples:
(1) When sodium bicarbonate (sodium hydrogen carbonate) reacts with hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride is formed along with carbon dioxide and water.
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is also known as baking soda, baking powder, bread soda or bicarbonate of soda.
(2) When sodium carbonate (sodium hydrogen carbonate) reacts with sulphuric acid, sodium sulphate is produced along with carbon dioxide and water.
Characteristic test for carbon dioxide gas:
When carbon dioxide, produced in this or above reactions, is passed through lime water, lime water turns milky because of formation of insoluble calcium carbonate. Calcium carbonate formed in this reaction as white precipitate.
The chemical name of lime water is calcium hydroxide.
This is the characteristic test for carbon dioxide gas.
In this reaction; downwards arrow indicates the formation of precipitate.
When the excess of carbon dioxide gas is passed through the solution of this reaction mixture, the white (milky) colour of lime water vanishes out. This happens because of formation of calcium hydrogen carbonate (calcium bicarbonate) which is soluble in water.
Neutralization Reaction
How do Acids and Bases React with each other?
Acid and base react with each other and produce respective salt and water.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
Examples:
Reaction of hydrochloric acid with base:
When hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide, sodium chloride and water are formed.
When hydrochloric acid reacts with calcium hydroxide, calcium chloride and water are produced.
Reaction of Sulphuric Acid with Base:
When sulphuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide, it produces sodium sulphate and water.
When sulphuric acid reacts with magnesium hydroxide, magnesium sulphate and water are formed.
Reaction of nitric acid with base:
When nitric acid reacts with calcium hydroxide, calcium nitrate and water are formed.
Reaction an acid with a base is called neutralization reaction. Since, in such reactions acid neutralizes the base.
Use of Neutralization Reaction:
Acidity:
Acidity is a medical condition which resulted in cramp in stomach and uneasiness to a person. Acidity is one of the common results of overeating or indigestion. In the case of over-eating our stomach produces more acid to digest the food resulting in the form of acidity.
In the case of acidity doctors give antacid. Antacid is a medicine comes in the form of suspension or tablet. Antacid means anti of acid, i.e. substance which works against acid. Antacid is a base. Generally milk of magnesia (a base) is used as antacid in the condition.
Antacid (base) goes in stomach and neutralizes the excess acid produced. After neutralization of excess acid in our stomach, person suffering from acidity feels relax.
Bee sting:
Honey bee pushes venom through its sting in skin. The venom so injected is acidic. Thus by applying substance containing base or mild base over the stung area gives relief to the victim by neutralizing the effect of acid of venom.
Wasp sting:
Wasp sting is alkaline. Thus by applying lemon, vinegar or other mild acid over the stung area neutralizes the effect of alkali pushed in the form of venom through sting, give relief to the victim person.
Chemical Properties-4
Reaction of Metallic Oxide with Acids
Metal oxides are said to be basic oxides. This means metal oxides are basic in nature. Thus when a metal oxide reacts with acids, respective salt and water are produced.
Acid + Metal Oxide → Salt + Water
Examples:
(1) When hydrochloric acid reacts with copper oxide, copper chloride and water are formed.
The color of copper oxide is black in color. After reaction with hydrochloric acid, the solution becomes blue green because of formation of copper chloride.
(2) When hydrochloric acid reacts with calcium oxide, calcium chloride and water are formed.
Reaction of a Non-metallic Oxide with Base
Non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature. For example, carbon dioxide is a non-metallic oxide, when carbon dioxide dissolve in water it produces carbonic acid.
Thus, when a non-metallic oxide reacts with base, it forms respective salt and water.
Non – metallic oxide + Base → Salt + Water
Example:
(1) When carbon dioxide which is a non-metallic oxide, reacts with sodium hydroxide, it gives sodium carbonate and water.
(2) When sulphur dioxide, which is a non-metallic oxide, reacts with sodium hydroxide, it gives sodium sulphite and water.
Common in Acid and Base
What do all Acids and All Bases have in Common?
Acids when react with metals, produces hydrogen gas. This means it is appears that all acid contains hydrogen. For example: Hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, Nitric acid, acetic acid, etc.
But all compounds which contain hydrogen are not acid. For example: glucose, alcohol, etc. While glucose and alcohol contain hydrogen but they are not acid.
On the other hand a base also produces hydrogen gas when reacts with a metal. This also suggests that a base also contains hydrogen.
Thus, it can be concluded that acid and base both contains hydrogen atom in any form.
Acids conduct electricity in aqueous solution
Conduction of electricity in aqueous solution depends upon free ions present in solution. When an acid is dissolved in water, it conducts electricity.
The conduction of electricity through aqueous solution of acids suggests that acids produce hydrogen ions [H+(aq)] in solution. These hydrogen ions are responsible for conduction of electricity through solution.
What happens to an Acid or a Base in Water Solution?
Acid in water solution
When an acid is dissolved in water it gives hydrogen ion [H + (aq)].
Examples:
When hydrochloric acid (HCl) is dissolved in water it gives hydrogen ion (H+) and chloride ion (Cl—).
When sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is dissolved in water it gives hydrogen ion (H+) and sulphate ion (SO4— —).
When nitric acid (HNO3) is dissolved in water it gives hydrogen ion (H+) and nitrate ion (NO3—).
When acetic acid (CH3COOH) is dissolved in water it gives acetate ion (CH3COO—) and hydrogen ion (H+).
Is an acid produces hydrogen ion in absence of water?
Acid does not dissociate hydrogen ion without water. To dissociate hydrogen ion water is necessary for acid.
This can be proved using an experiment.
When sodium chloride reacts with sulphuric acid, it produces dry hydrochloric acid gas.
When a dry blue litmus paper is brought near the evolved hydrochloric acid gas no change is observed in the colour of litmus paper. But when a moist litmus paper is brought near the hydrochloric acid gas, litmus paper turns to red.
This suggest that water is necessary to dissociate hydrogen ion [H+(aq)] for an acid.
When an acid is dissolved in water, hydrogen ion (H+) dissociated by acid get combined with water molecule and produced hydronium ion (H3O+). This happens because hydrogen ion cannot exist alone.
The intermediate reaction to give hydrogen ion by hydrochloric acid in water can be shown as follows:
HCl + H2 ⇒ H+ + H2O + Cl— ⇒ H3O+ + Cl—
This may also be written as:
H+ + H2O ⇒ H3O+
Thus, hydrogen ion is always written as H+(aq). After writing the symbol of hydrogen ion the word ‘aq’ is always written in the bracket. This shows the presence of water.
Or hydrogen ion is written as Hydronium ion (H3O+).
Examples:
Base in Water Solution
When a base is dissolved in water it dissociates hydroxide ions (OH—).
Example:
When sodium hydroxide is dissolved in water it produces hydroxide ion.
When calcium hydroxide is dissolved in water, it produces hydroxide ion.
When potassium hydroxide is dissolved in water it produces hydroxide ion.
When ammonium hydroxide is dissolved in water, it produces hydroxide ion.
Magnesium hydroxide, a base, is not fully soluble in water, but it gives hydroxide ion when dissolved in water.
Ammonia gas is basic in character and soluble in water. When ammonia gas is dissolved in water it gives ammonium hydroxide. This ammonium hydroxide dissociates hydroxide ion.
Is a base produce hydroxide ion in absence of water?
Similar to acid base also not produced hydroxide ion in absence of water. However base produce hydroxide ions in molten state. This is the cause that a base conducts electricity in molten form.
How neutralization reaction takes place:
Acid produces hydrogen ions and base produces hydroxide ions. Thus when an acid and base react, hydrogen ions produced by acid and hydroxide ions produced by base combined together and water molecules are formed. Because of formation of water molecule by hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion reaction mixture becomes neutralize. Along with water molecule respective salt is also formed in a neutralization reaction.
In other words hydrogen ions of an acid and hydroxide ions of a base neutralize each other.
Acid + Base ⇒ Salt + Water
Where, X is anion (negative ion) of an acid and M is the cation (positive ion) of a base.
Strenght of Acid and Base
How strong are Acid or Base Solutions?
In distilled water, concentration of hydrogen ions and concentration of hydroxide ions are equal. Thus, distilled water is neither acidic nor basic.
If the hydrogen ions concentration is higher than that of hydroxide ions concentration in a solution, the solution is acidic. And if the hydroxide ions concentration is higher than that of the hydrogen ions, the solution is called basic.
Acid base indicator can only distinguish between acid and base. But an acid base indicator does not tell about the strength of an acid or base, i.e. it does not tell that how much strong or powerful or potential an acid or base.
Since, an acid produces hydrogen ions and a base produces hydroxide ions in their aqueous solution, thus by knowing concentration of hydrogen ions quantitatively the strength of an acid or base can be determined.
Acid which has more hydrogen ion concentration is said to be stronger and those which produce less hydrogen ions is said to be weaker. Similarly, a base which has more hydroxide ions concentration is said to be stronger base and those which produces less hydroxide ions is said to be weaker base.
Example:
Same concentration of hydrochloric acid produces more hydrogen ions compare to acetic acid of same concentration. Thus, hydrochloric acid is stronger acid than that of acetic acid.
pH scale:
The concentration of hydrogen ion in a solution can be determined using pH scale.
In the word pH, p stands for potency or power and H stands for Hydrogen ions. p came from German word ‘potenz’ which means power. In totality it can be said that pH means power of an acid.
pH scale is a tool using which hydrogen ion concentration is measured.
Definition of pH:
pH is defined as the decimal logarithm of the reciprocal of the hydrogen ion activity (aH+) in a solution.
pH scale works on the value from 0 to 14 (zero to fourteen).
0 (zero) value on pH scale indicates highly acidic (strongest acid)
7 (seven) value on pH scale indicates the neutral solution
14 (fourteen) value on pH scale indicates highly basic (strongest base)
Strength of acid, i.e. acidity increases with decreasing of value on pH scale from 7 (seven) to (0) zero
Strength of base, i.e. basicity increases with increasing of value on pH scale from 7 (seven) to 14 (fourteen)
Thus, by knowing the value of on pH scale strength of an acid or a base can be determined.
Universal indicator:
Universal indicator is a mixture of many compounds. It composes generally water, propane-1-ol, phenolphthalein, sodium salt, sodium hydroxide, methyl red, bromothyomol blue monosodium salt and thyomol blue monosodium salt. Universal indicator exhibits colour in colour of solution over a pH value range from 1 to 14. Changing of the range of pH value indicates the acidity or basicity of the solution.
A colour chart is supplied with universal indicator. Different colours in the given chart shows pH values range from 1 to 14.
Universal indicator comes in solution form and paper strips form both.
When universal indicator paper strip is dipped in given solution, colour of paper strip changes. This changed colour is matched with the given chart and value of pH is obtained. According to the value of pH observed acidity or basicity of the given solution is determined.
pH value of some of the common liquid is given here.
| pH value of some common liquids | |
|---|---|
| pH | Name of Liquids |
| 0 | Battery acid |
| 1 | Sulphuric acid, Gastric juice (1.2) |
| 2 | Lemon juice, vinegar |
| 3 | Orange juice, soda |
| 4 | Totamo juice, acid rain |
| 5 | Black coffee, bananas |
| 6 | Urine, milk |
| 7 | Pure water, blood (7.4) |
| 8 | Sea water, egg |
| 9 | Baking soda |
| 10 | Milk of magnesia |
| 11 | Ammonium solution |
| 12 | Soapy water |
| 13 | Bleach, oven cleaner |
| 14 | Liquid drain cleaner, sodium hydroxide solution |
Importance of pH in Everyday Life
Are plants and animals pH sensitive?
All plants and animals are sensitive towards pH. Living organism works within the narrow range of pH. Our body also works within the narrow range of pH of 7.0 to 7.8 only. If this pH range increases or decreases, living organism find it difficult to survive.
We have to face the problem of acidity if pH value of our stomach decreases, i.e. becomes more acidic. If the pH value of our mouth decreases, our tooth starts decaying. If the pH value of soil decreases or increases than normal, soil becomes infertile. If the pH value of river water decreases, fish starts dying. Hence, it is clear that living organisms are sensitive towards the value of pH.
pH of soil for healthy growth of plants
Plants grow properly and gives proper yield if the soil is neither acidic nor basic i.e. neutral. This means pH of the soil should be equal to 7 for healthy growth of plants.
Often wrong harvesting and use of excess fertilizers increase or decrease the pH of soil from normal. This affects the growth of plants which is resulted in lower yield.
If pH value of soil is found lower than 7, i.e. soil becomes acidic; soil is treated with calcium oxide, calcium hydroxide or chalk. After treatment excess acid present in soil neutralizes and soil becomes fertile again.
Similarly, often pH value of soil becomes greater than 7, i.e. becomes basic. In such condition also soil is treated with neutral manure or compost or pyrite or gypsum which neutralizes the basic nature of soil.
Government gives the facility to farmers to get their soil checked at regular basis.
pH in our digestive system
Walls of our stomach produce hydrochloric acid which kills germs present in food if any. This hydrochloric acid also helps in the digestion of food we eat.
Digestion takes place in our stomach in acidic medium. The pH value of our stomach is near 1.2. But in the case of overeating the receptors of walls of stomach get wrong message and start producing more acid. This decreases the pH value of our stomach, resulting in the condition of hyperacidity. This creates problems and we feel burning sensation and uneasiness, and sometimes vomiting tendency also.
To neutralize excess acid produced by stomach, an antacid a medicine is taken orally. This neutralizes the extra acid produced by our stomach and we feel comfortable. Milk of magnesia is taken as medicine which is a mild base.
pH change as the cause of tooth decay
Normal pH value of our mouth is about 6. This is because of saliva produced by glands present in our mouth. This means that medium of our mouth is slightly acidic.
Tooth’s enamel is made of calcium phosphate. This is insoluble in water but start corroding because of acid. Some times food particles get trapped between teeth gap. After some time bacteria present in mouth start acting upon carbohydrate, which is a type of sugar, present in food items and produced acid. This acid decreases the pH value of mouth from 6. This acid starts decaying the enamel of tooth. After degradation of enamel teeth becomes sensitive and bad breadth starts coming out of the mouth. If decaying of tooth is not stopped timely, it is resulting in tooth loss.
The action of bacteria can be prevented by brushing of teeth using toothpaste. Toothpaste is basic in nature and it neutralizes the more acid produced in mouth because of bacteria.
Self defense by animal and plants through chemical warfare:
All living organism got self defense tools as a gift from nature. For example deer, buffalo, cows, etc. has long and sharp horn, lizard can change its colour, bee has sting, etc.
Defense weapon of bee:
Honey bees are armed with chemical sting as defense tool. Honey bee contains acid in their sting. When a person is stung by honey bee, honey bee injects acid and pushes and leaves its sting in skin. Because of acid present in sting, victim feels pain near the stung area. Area of stung get swollen after some time.
Honey bee sting contains methonic acid, so rubbing of baking soda, toothpaste or other mild base at the stung area neutralizes the effect of acid and gives relief to the victim from pain.
Defense weapon of ant:
Ant has bite as their defense tool. Ant bite also contains methanoic acid similar to honey bee. Thus, by rubbing of mild base near the ant bite gives relief to the victim. However, there are some type of ant found in world whose bite is very dangerous and immediately hospitalization is required in such case.
Plants with defense weapon:
Some plants are armed with sting as defense tool, such as nettle. Plants of nettle has sting. A person who touches the nettle leaves gets stung similar to honey bee. Nettle leaves also contain methanoic acid, which resulting in pain and irritation near the stung area. In such case also rubbing of mild base, such as slaked lime, baking powder, etc. gives relief to the victim from pain.
class/std Ten Science
Acid, Base & Salt
What is Salt
Most common salt is common salt, i.e. sodium chloride (NaCl). Salt is produced in laboratory by the neutralization reaction of acid and base. Potassium sulphate, sodium sulphate, sodium nitrate, sodium carbonate, etc. are examples of some salts other than sodium chloride.
A salt contains two types of ions, i.e. positive and negative. For example in NaCl, Na+ is positive ion and Cl — is negative ion.
Generally, a salt is neutral in nature as a salt is formed by the combination of cation and anion.
Example:
When sodium hydroxide (a base) reacts with hydrochloric acid, water and sodium chloride (a salt) are formed.
In this reaction sodium ion from sodium hydroxide and chloride ion from hydrochloric acid form sodium chloride by combining together. Hydroxide ion (OH—) from Sodium hydroxide, and hydrogen ion (H+) from hydrochloric acid are replaced and combine together to form water.
In similar manner lot of salts are formed.
Naming of salt:
Salts are named after the acid and base because of which they formed.
Cation, which is first part of salt is named after base and anion, which is second part of salt is named after acid.
Examples:
(1) Sodium chloride (a salt) is formed after the neutralization reaction of sodium hydroxide (a base) and hydrochloric acid (an acid). It got its name as sodium (first part) after sodium hydroxide and chloride (second part) after hydrochloric acid (hydrogen chloride).
(2) Calcium nitrate is formed after the reaction of calcium hydroxide and nitric acid. Therefore, in Calcium nitrate (a salt), calcium comes from calcium hydroxide and nitrate comes from the nitric acid.
(3) Potassium sulphate is formed after the reaction between potassium hydroxide and sulphuric acid (hydrogen sulphate). In this salt potassium comes after potassium hydroxide and sulphate comes after the sulphuric acid.
Thus,
(a) Because of hydrochloric acid, chloride salts are formed.
Example:
sodium chloride (NaCl), calcium chloride (CaCl2), potassium chloride (KCl), Magnesium chloride (MgCl2), Copper chloride (CuCl2), Zinc chloride (ZnCl2), Aluminium chloride (AlCl3), Barium chloride (BaCl2), etc.
(b) Salts formed by sulphuric acid (H2SO4) are called sulphate salts.
Example:
Sodium sulphate (Na2SO4), potassium sulphate (K2SO4), Calcium sulpahte(CaSO4), Magnesium sulphate(MgSO4), copper sulphate(CuSO4), zinc sulphate(ZnSO4), Iron sulphate(FeSO4), Aluminium slupahte(Al2(SO4)3), Ammonium sulpahte ((NH4)2SO4), etc.
(c) Salts formed by nitric acid are called nitrate.
Example:
Sodium nitrate(NaNO3), Calcium nitrate (CaNO3), Potassium nitrate(KNO3), Ammonium nittrate (NH4NO3), Beryllium nitrate (BeNO3), Magnesium nitrate (Mg(NO3)2), Zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)2), etc.
(d) Salts formed because of carbonic acid are called carbonates.
Example:
Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), Calcium carbonate (CaCO3), Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3), Potassium carbonate (K2CO3), Beryllium carbonate (BeCO3), Copper carbonate(CuCO3), etc.
(e) Similarly, salts formed by acetic acid are called acetates.
Common Characteristics of salts:
Most of the salts are solid.
Salts can be transparent or opaque.
Salts are generally soluble in water.
Most of the salts dissociate ions in aqueous solution, thus they conduct electricity in their aqueous solution. Salts in their molten state also conduct electricity.
A salt has two parts, one is cation (positively charged) and other is anion (negatively charged).
Since, salts are formed after the neutralization reaction, thus, a salt is electrically neutral in general.
Most of the salts are coulerless, but many of them are coloured.
Examples of some coloured salts:
Yellow (sodium chromate)
Orange (potassium dichromate)
Red (potassium ferricyanide)
Mauve (cobalt chloride hexahydrate)
Blue (copper sulfate pentahydrate, ferric hexacyanoferrate)
Purple (potassium permanganate)
Green (nickel chloride hexahydrate)
Colorless (magnesium sulfate heptahydrate) may appear white when powdered or in small pieces
class/std Ten Science
Acid, Base & Salt-
Family of Salt
Salts are formed by the reaction of acids and base. And a salt contains positive and negative radicals both. On the basis of positive and negative radicals, salts can be categorized into family.
If two salts have same positive or negative radicals, they are called to be of same family.
In other words, if salts formed by the reaction of same acid with different bases, then all salts so formed belong to the same family. On the other hand if salts formed by the reaction same base with different acids, then all salts so formed have same negative radicals, and all such salts are called to be belonged to the same family.
Example:
In Sodium chloride and sodium sulphate, sodium which is positive radical is same in both of the salts. Thus, sodium chloride and sodium sulphate belongs to the sodium family.
Similarly, in sodium chloride and potassium chloride, chloride which is negative radical is same. Thus, sodium chloride and potassium chloride both belong to chloride family.
Examples:
Salts belong to chloride family:
All salts having chloride as negative radical belong to chloride family. For example: Sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, copper chloride, beryllium chloride, aluminium chloride, etc. belong to the same family, i.e. chloride family.
Salts belong to sulphate family:
All salts having sulphate ions as negative radical belong to the sulphate family. For example: sodium sulphate, potassium sulphate, magnesium sulphate, aluminium sulphate, copper sulphate, etc.
Salts belong to nitrate family:
All salts having nitrate ions as negative radical belong to the same family, i.e. nitrate family. For example: sodium nitrate, calcium nitrate, potassium nitrate, aluminium nitrate, copper nitrate, etc.
Salts belong to sodium family:
All salts having sodium ions as positive radical belong to the same family, i.e. sodium family. For example: sodium chloride, sodium sulphate, sodium nitrate, etc.
Salts belong to the copper family:
All salts having copper ion as positive radical belong to the copper family. For example: copper sulphate, copper chloride, copper nitrate, etc.
Similarly all carbonates belong to same family of salt, i.e. carbonate family. For example: copper carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, etc.
pH of Salts
Salts are formed by the neutralization reaction between acid and base consequently pH of salts should be equal to 7, i.e. salts should be neutral.
But, actually most of the salts have pH value less than or more than 7. pH of salts may be equal to 7 or more than seven or less than seven. This means salts may be neutral, acidic or basic.
Salts which are formed by the reaction of same strength of acid and base are neutral in nature and have pH value equal to 7. Such salts are called neutral salts.
Neutral salts i.e. salts having pH value equal to 7:
Salts produced after the reaction of a strong acid with a strong base, is neutral in character. For example: Sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium sulpahte, potassium sulphate, etc.
Examples of formation of neutral salt with pH value equal to 7
When sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride is formed. Since, sodium hydroxide is a strong base and hydrochloric acid is a strong acid, thus sodium chloride formed in this reaction is neutral in character. pH value of sodium chloride (common salt) is about equal to 7.
Similarly, sodium sulphate (a salt) formed by the reaction between sodium hydroxide and sulphuric acid, is neutral in chatater. Because sodium hydroxide is a strong base and sulphuric acid is a strong acid. pH value of sodium sulphate is nearly equal to 7, i.e. sodium sulphate is neutral in character.
Acidic salt i.e. salts having pH value less than 7:
(a) When a strong acid reacts with a weak or mild base, an acidic salt is formed. This happens because weak base could not neutralise the strong acid fully i.e. only partial neutralization takes palce. For example ammonium sulphate, ammonium chloride, etc.
When ammonium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid, ammonium chloride is formed along with water.
In this reaction, ammonium hydroxide, which is a weaker base cannot able to neutralize hydrochloric acid, which is a strong acid fully. And some acidic character remains present in salt so formed. Thus, ammonium chloride is acidic in nature, and its pH value is less than 7.
(b) When ammonium hydroxide reacts with sulphuric acid, ammonium sulphate ((NH4)2SO4) is formed.
In this reaction ammonium hydroxide is weaker base than sulphuric acid resulting ammonium hydroxide could not neutralizes sulphuric acid completely. Thus, salt ammonium hydroxide formed in this reaction is acidic in nature and its pH value is less than 7.
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), Sodium hydrosulphide or sodium hydrogen sulphide (NaHS), Sodium bi sulphate (NaHSO4), monosodium phosphate(NaH2PO4), disodium phosphate, etc. are examples of some acidic salts.
Basic salt i.e. salts having pH value more than 7:
Basic salts are formed when a strong base reacts with weaker acid. pH value of basic salt is more than 7. This happens because weaker acid could not neutralize strong base completely. And because of partial neutralization of base a basic salt is formed. For example: sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), magnesium carbonate (MgCO3), potassium carbonate (K2(CO3)2), sodium acetate (NaCH3COO), calcium acetate (Ca(CH3COO)2), etc.
Examples of formation of basic salts:
(a) When Carbonic acid (H2CO3) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), sodium carbonate is formed.
Since, carbonic acid is a weaker acid than sodium hydroxide (a base), thus sodium carbonate (salt) so formed in this reaction, is a basic salt. And pH value of sodium carbonate is greater than 7.
(b) When acetic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide, sodium acetate is formed.
Since, sodium hydroxide is stronger base than acetic acid, thus salt (sodium acetate) formed in this neutralization reaction is basic in nature and its pH value is more than 7. This happens because acetic acid does not neutralize sodium hydroxide completely
Common Salt - Sodium Chloride
The chemical name of common salt is sodium chloride. We use sodium chloride (common salt) in our food. Sodium chloride is one of the essential things of animal life. A small quantity of sodium chloride is essential for all known living creatures. Salt is responsible for regulation of water (fluid balance) in our body. In the case of dehydration, our body looses excess salt, and we fell ill. In the case of dehydration we have to rehydrate our body by taking fluid with essential salts. The sodium ion present in common salt is used for electrical signaling in the nervous system of our body. Since salt is one of the essential things for survival thus salt has been considered one of the most valuable things in human history.
Salt movement: Dandi March:
In our history to get freedom from English Salt was one of the most important symbolic weapons. Mahatma Gandhi performed Dandi March and started Salt Movement. Dandi is a place inear sea cost in Gujrat.
Obtaining of Sodium Chloride (Common salt):
In laboratory: Common salt can be obtained from reaction of sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid in laboratory.
From Sea water: Water from rivers flows into sea. This water carries many salts which finally remains dissolved in sea water. Common salt (sodium chloride) is separated from sea water by evaporating sea water.
From Rocks: In several parts of world solid salt are found in the form of deposit. When seas of bygone ages dried up, salt dissolved in sea water were formed in the form of beds of rock salt. From these beds salt are mined like coal.
Salts obtained from sea water or mined in the form of rock salt contain many impurities. The large crystals of salts so obtained are generally appears brown in colour because of impurities. These impurities are refined by many processes to obtain pure common salt (sodium chloride).
Some Uses of Common salt (Sodium chloride):
Manufacturing of many chemicals, such as sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), sodium carbonate (washing soda), hydrochloric acid, chlorine, etc.
Common Salt (sodium chloride) is used in manufacturing of soap.
Sodium chloride is used in the flocculation (a process in which colloids come out of suspension in the form of floc or flakes by the addition of a clarifying agent).
Used as food preservative.
Common salt makes our food tasty.
Sodium chloride is used in dairy industry. Common salt is added to cheese as a color-, fermentation-, and texture-control agent.
Sodium chloride is used in textiles and dyeing industries. In these industries brine (solution of sodium chloride in water) is used to rinse separate organic contaminants.
Sodium chloride is used in wood and paper pulp industries. This is used to bleach wood pulp.
Common Salt (Sodium Chloride): A raw material for chemicals
Sodium chloride is a raw material for many chemicals which are used in our daily life. For example: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), Baking soda, washing soda, bleaching powder, etc. are obtained from sodium chloride.
class/std Ten Science
Acid, Base & Salt
Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide is also known as caustic soda or Iye. Sodium hydroxide comes in the form of pellets, flakes, granules, and solution in market. Sodium hydroxide is a strong base and caustic in nature.
Production of sodium hydroxide from sodium chloride
CHLOR-ALKALI PROCESS:
Sodium hydroxide is obtained by the Chlor-Alkali Process. In this Chlor stands for chlorine and alkali stands for sodium hydroxide, that’s why this is called chlor-alkali process.
In chlor-alkali process electric current is passed through the brine (aqueous solution of sodium chloride). After passing the electric current through brine, sodium hydroxide solution is formed near cathode. In this process chlorine gas is deposited at anode and hydrogen gas is deposited at cathode.
Chlor-alkali process – fig1
Ref: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Membrane_cell.jpg#filelinks
Uses of products obtained in CHLOR-ALKALI PROCESS:
Sodium hydroxide:
In making of soaps
In making of detergents
In making of paper
In making of artificial fibres
In de-greasing of metals, etc.
Chlorine:
In water treatement
Mixed with swimining pool water
In making of PVC
In making of disinfectants
In making of CFCs
In making of pesticides
Hydrogen:
In making of fuels
Margarine
In making of ammonia for fertilizers
Chlorine + Hydrogen:
Chlorine and hydrogen together is used in making of hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid is also known as Muriatic Acid and spirits of salt.
Hydrochloric acid is used in cleaning of steel, making of ammonium chloride, in making of medicines and cosmetics, etc.
Chlorine + Sodium hydroxide:
Chlorine and sodium hydroxide together is used in making of bleach for household bleaches and bleaching of fabrics, etc.
Bleaching Powder
Bleaching powder is manufactured using chlorine which is obtained as one of the product in CHLOR-ALKALI Process.
The general chemical formula of bleaching powder is CaOCl2 and its chemical name is calcium oxychloride. Bleaching powder is also known as chloride of lime.
Production of bleaching powder:
When chlorine gas is passed over dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)2], bleaching powder is formed.
Physical Properties of bleaching powder:
Bleaching powder is a yellowish white solid.
Bleaching powder is soluble in water.
Bleaching powder gives strong smell of chlorine.
Chemical Properties of bleaching powder:
When bleaching powder reacts with sulphuric acid, it gives calcium sulphate, chlorine and water.
When bleaching powder reacts with hydrochloric acid, it gives calcium chloride, chlorine and water.
Solution of bleaching powder is basic in character.
When bleaching powder is dissolved in water, it gives calcium hydroxide and hypochlorous acid. Instead of formation of an acid in aqueous solution, aqueous solution of bleaching powder turns red litmus paper blue. This happens because hypochlorous acid is very weak acid while calcium hydroxide is stronger base than hypochlorous acid. Thus, solution of bleaching powder shows basic character.
In bleaching powder, the word ‘bleach’ means decolouration, whiten or disinfectant. Bleaching powder is a powerful oxidizing agent, as it contains chlorine, thus because of oxidation bleaching powder acts as an decoloring agent, whitening agent and disinfectant.
Use of bleaching powder:
- Bleaching powder is used in whitening of cloth and in removing of stains.
- Bleaching powder is used as disinfectant, algae cleaner, moss remover, weed-killers, etc.
- Bleaching powder is used in purification of water as disinfectant.
- Bleaching powder is used in swimming pool water as disinfectant.
- In manufacturing of chloroform.
- Bleacing powder is used as oxidising agent in many chemical industries.
- Bleaching powder is used in bleaching of cotton in textile industries.
- Bleaching powder is used in paper industries in bleaching of wood pulp.
Baking Soda (Sodium Bicarbonate)
Baking soda is another chemical obtained from sodium chloride. The chemical name of baking soda is sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3). Other name of baking soda is bread soda, cooking soda, bicarbonate of soda, sodium bicarb, bicarb of soda and bicarb, etc.
Baking soda is used in baking of food and making of food tasty. It is also used in faster cooking.
Production of baking soda (sodium bicarbonate):
(a) By Solvay Process: Baking soda (Sodium bicarbonate) is produced by reaction of sodium chloride, carbon dioxide and ammonia. This process is known as Solvay Process.
(b) When carbon dioxide is passed through the solution of sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate is produced. After passing more carbon dioxide, this sodium carbonate (baking soda) changes into sodium bicarbonate.
Properties of sodium bicarbonate:
Sodium bicarbonate is amphoteric in nature. An amphoteric compound reacts in similar way with an acid and a base both.
Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid. Sodium bicarbonate appears as powder but actually it is crystalline.
Sodium bicarbonate is sparingly soluble in water.
Sodium bicarbonate when dissolved in water, gives carbonic acid and hydroxide ion. Since carbonic acid is weak acid, thus solution of sodium bicarbonate is alkaline in nature.
When sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) put under thermal decomposition it gives sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide and water.
On continuous heating sodium carbonate produced in thermal decomposition of sodium bicarbonate converts into sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. This reaction is called dehydration reaction.
As it gives carbon dioxide, which put off fire, sodium bicarbonate is used as fire extinguisher or fire suppression agent. It is also known as BC powder.
Some Uses of sodium bicarbonate (Baking soda):
- Baking soda is used in cooking. Baking soda on heating produced carbon dioxide which makes barter soft and spongy.
- Sodium bicarbonate is a base thus it is used as antacid.
- Sodium bicarbonate is also used in the treatment of overdose of aspirin.
- Mixing of sodium bicarbonate in water is exothermic. This character makes it an antiseptic.
- It is used in toothpaste. This whitening the teeth and remove plaque.
- Sodium bicarbonate is also used as cleaning and scrubbing.
- It is used as bio-pesticide.
- Sodium bicarbonate is used in cattle feed as it acts as buffering agent for rumen.
- Sodium bicarbonate is used as fire extinguisher for mild fire.
- In fire extinguisher it is used as one of the component. In fire extinguisher sodium bicarbonate is allowed to react with sulphuric acid kept in a separate chamber, in the condition of fire. Reaction of sodium bicarbonate and sulphuric acid gives carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide so produced is thrown over the fire, which cover the fire and stop the supply of oxygen. This process put off the fire. This fire extinguisher is also known as soda-acid fire extinguisher.
Washing Soda (Sodium Carbonate)
Washing soda is another important chemical obtained from sodium chloride (common salt). The chemical name of washing soda is sodium carbonate (Na2CO3). Washing soda is the sodium salt of carbonic acid. As its name says, washing soda is used in washing.
Production of washing soda:
By Solvay Process:
In Solvay process first sodium bicarbonate is produced. This sodium bicarbonate on heating gives sodium carbonate (washing soda).
Sodium carbonate obtained in this Solvay process is dry, so it is also called soda ash.
The Solvay process got its name after Ernest Solvay who developed this process in 1861. Earnest Solvay was an industrial chemist and belonged to Belgian.
Soda ash (anhydrous soda) to washing powder:
By treating with water anhydrous sodium carbonate (soda ash) is converted into washing soda.
Since, washing power contains 10 (ten) water molecules, thus is called sodium carbonate decahydrate.
Properties of washing soda:
- Sodium carbonate is a crystalline transparent solid.
- Where most of the carbonates are insoluble in water, sodium carbonate is soluble in water.
Some Uses of sodium carbonate (Washing soda):
- Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is used as detergent even today in many rural areas.
- Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is used in making of detergent cake and powder.
- Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is used in removing of permanent hardness of water.
- Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is used for making many types of chemicals such as borax.
- Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is used in glass and paper industries
Water of Crystallisation
Are the crystals of salts really dry?
Crystals of salts appear dry. But many salts contain some water molecule. This water molecules contain by crystals of slats is known as water of crystallization. Salts that contain water molecules are known as hydrated salts. For example: copper sulphate, gyspsum, sodium carbonate, etc.
Example: (1)
Sodium Carbonate (Washing soda):
Sodium carbonate which is also known as washing soda, contains 10 (ten) water molecules, because of this sodium carbonate is called sodium carbonate decahydrate. Sodium carbonate which does not contains any water molecule is called anhydrous sodium carbonate. Anhydrous sodium carbonate is also known as soda ash.
The chemical formula of sodium carbonate is Na2CO3 . 10 H2O
Sometimes, crystals of sodium carbonate contain seven water molecules. In such case chemical formula of sodium carbonate is written as Na2CO3 . 7 H2O and it is called sodium carbonate heptahydrate.
Example: (2)
Copper Sulphate
Crystals of copper sulphate appears blue because it contains 5(five) water molecules. This is the cause that chemical formula of copper sulphate is CuSO4 . 5 H2O.
When crystals of copper sulphate is heated, it loses its water molecule and its colour and becomes grey white.
But when water is added to anhydrous copper sulphate, or it exposes to moisture present in air, it turns blue again.
Example: (3)
Ferrous Sulphate:
Crystals of ferrous sulphate appears bluish green in colour. This colour in ferrous sulphate is due to the presence of water molecule in it. Crystals of ferrous sulphate contains 7(seven) water molecules. Because of it the chemical formula of ferrous sulphate is FeSO4 . 7 H2. Since ferrous sulphate contains seven (7) water molecules, thus it is also called ferrous sulphate heptahydrate.
Example: (4)
Gypsum:
The chemical formula of Gypsum CaSO4 . 2 H2. The chemical name of gypsum is calcium sulphate dehydrate as it contains two molecules of water. Gypsum is also a hydrated salt. It contains two molecules of water.
Plaster of Paris
Plaster of paris is also known as gypsum plaster. The chemical formula of plaster of paris is CaSO4 . ½ H2O. This got its name ‘Plaster of Paris’ because a large gypsum deposit at Montmartre in Paris.
Conversion of Plaster of Paris from gypsum:
Plaster of Paris is obtained by heating of gypsum at about 1500C. At this temperature 1.5 molecules of water is evaporated and gypsum turns into plaster of Paris.
Rehydration of Plaster of Paris:
When plaster of Paris is rehydrated by mixing of water, it turns into gypsum and when this gypsum left open, it starts drying after about 10 minutes and in about 45 minutes it sets as solid. In about 72 hours it dried completely.
The unique property of quick drying and setting into solid after some hours makes plaster of Paris very useful.
Properties of Plaster of Paris:
Plaster of Paris is a white powder.
Mixing of water into the powder of Plaster of Paris is exothermic.
Some Uses of Plaster of Paris:
- Plaster of Paris is used in medical treatment. It is used to cover as plaster in the case of fractured bones. Mounding of plaster of Paris over the part of body after setting of bones ensures to keep bones at right place.
- Plaster of Paris is used for making beautiful and designer false ceiling and other room interiors.
- Plaster of Paris is used in casting into clay molds.
- Plaster of Paris is used in making toys, and other decorative materials.
NCERT InText Solution:1
Question: 1: You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the contents of each test tube?
Answer: An acid solution turns red litmus paper blue and a basic solution turns blue litmus paper red. While distilled water does not act upon litmus paper.
Step: 1: Solution in test tube which changes red litmus paper blue is acid.
Step: 2: Now, blue litmus paper which is changed blue by acid is dipped in rest of the two test tubes one by one. Solution which changes the blue litmus paper red is basic solution.
Step: 3: Third one solution in test tube left, which does not change either red litmus blue or blue litmus paper red is identified as distilled water.
Question: 2: Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Answer: Metals on reaction with acid produces hydrogen gas and respective salt. Copper is a metal and brass is an alloy of copper metal. Thus, copper and brass reacts with acid and form hydrogen gas.
Curd and other sour substances contain acid. That’s why curd and other sour substances are not kept in the brass and copper vessels.
Question: 3: Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Answer: When metal reacts with acid, it produces hydrogen gas.
Example:
When zinc metal reacts with hydrochloric acid, it produces hydrogen gas and zinc chloride.
When a burning candle or match stick is brought near the gas evolved, it burns with pop sound. Burning with pop sound proves the presence of hydrogen gas. Burning with pop sound is the characteristic test for hydrogen gas.
Question: 4: Metal compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Answer: Calcium carbonate produces carbon dioxide gas with effervescence along with calcium chloride when reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Since, carbon dioxide gas is used as fire extinguisher therefore, the given metal compound A is calcium carbonate.
Balanced chemical equation for above reaction:
Question: 5: Why do HCl, HNO3, etc., show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Answer: it is the presence of hydrogen ions in aqueous solution which is responsible for acidic character of a solution.
HCl, HNO3, etc., dissociate hydrogen ions in their aqueous solutions. And because of dissociation of hydrogen ions HCl, HCl, HNO3, etc. shows acidic characters.
While compounds like alcohol and glucose do not dissociate hydrogen ions in their aqueous solutions. Thus, in absence of hydrogen ions compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic characters.
Question: 6: Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity?
Answer: It is ions which are responsible for conduction of electricity in solution.
Acid dissociates hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions in their aqueous solution, thus because of presence of ions acid conducts electricity in their aqueous solutions.
Question: 7: Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour of the dry litmus paper?
Answer: It is the hydrogen ions or hydronium ions which is responsible for acidic character of a substance.
Dry HCl gas or any acid does not dissociate hydrogen ions in absence of water. That’s why dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper.
But, if litmus paper is moist, dry HCl gas changes the color of blue litmus paper red.
Question: 8: While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Answer: Dilution of acid or a base is highly exothermic. If water is added to concentrated acid for dilution, because of presence of acid in large amount, large amount of heat is evolved which will be dangerous as acid may splashes out and burn the skin.
Thus, it is recommended that always acid is added to water slowly and not water to acid.
NCERT InText Solution:2
Question: 9: How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted?
Answer: The concentration of acid decreases when diluted. Consequently concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) decreases when an acid is diluted.
Question: 10: How is the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide?
Answer: A base dissociates hydroxide ions in its aqueous solution. Thus, when excess base is dissolved in the solution of sodium hydroxide, which is a base, the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) will increase.
Question: 11: You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of this is acidic and which one is basic?
Answer: Hydrogen ions concentration increases with decrease in the value of pH.
Solution A has pH value equal to 6 and solution B has pH value equal to 8. Since, solution A has less pH value consequently solution A has more hydrogen ions concentration.
An acid has pH value less than 7 while a base has pH value more than 7. Since solution A has pH value less than 7, i.e. 6 thus, solution A is acidic.
And solution B has pH value more than 7, i.e. 8, thus solution B is basic.
Question: 12: What effect does the concentration of H+(aq) ions have on the nature of solution?
Answer: (1) Hydrogen ions concentration decides the acidic or basic nature of solution. The acidity of solution increases with increase in hydrogen ions concentration and decreases with decrease in hydrogen ions concentration.
Answer: (2) Nature of solution may be of two types:
(a) Concentrated or diluted
(b) Acidic or basic
(a) Concentrated or diluted:
A concentrated acid solution has more concentration of H+(aq) ions compare to diluted acid solution.
(b) Acidic or Basic
An acidic solution has more concentration of H+(aq) ions compare to hydroxide ions. While a basic solution has less concentration of H+(aq) ions compare to hydroxide ions concentration.
Question: 13: Do basic solution also have H+(aq) ions? If yes, then why are these base?
Answer: Yes basic solution also have H+(aq) ions.
But a base has less hydrogen ions concentration than hydroxide ions. It is the hydroxide ions concentration that decides that whether a solution is base or not.
Thus, solution which has also hydrogen ions but in less amount than hydroxide ions, are base.
Question: 14: Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
Answer: Quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate) are base which neutralizes acids.
Thus, if the soil condition is acidic, farmer would treat the soil of his field with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate) to neutralize the excess acid present in soil.
Question: 15: What is the common name of the compound CaOCl2?
Answer: The Common name of the compound CaOCl2 is bleaching powder.
Question: 16: Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Answer: When calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] is treated with chlorine, it yields bleaching powder (CaOCl2).
Question: 17: Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Answer: Sodium carbonate [Washing soda (Na2CO3)] is used for softening hard water.
Question: 18: What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Answer: When solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated, it produces sodium carbonate, water and carbon dioxide gas is formed.
Question: 19: Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Answer:
NCERT Exercise solution:1
Question: 1: A solution turns red litmus blue. It pH is likely to be
- 1
- 4
- 5
- 10
Answer: (d) 10
Explanation: A base turns red litmus blue. Solution having pH value more than 7 are base. Thus, here answer is (d) with pH value 10
Question: 2: A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky. The solution contains
- NaCl
- HCl
- LiCl
- KCl
Answer: (b) HCl
Explanation: egg shells are made of calcium carbonate. When calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, it produces carbon dioxide gas. When this carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water, lime water turns milky.
Thus, here answer is (b) HCl
Question: 3: 10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralized by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralize it will be
- 4mL
- 8mL
- 12mL
- 16mL
Answer: (d) 16mL
Explanation: Since 10 mL of NaOH solution requires 8 mL of HCl solution
Therefore, 20 mL of NaOH solution will require 8 x 2 = 16 mL of HCl solution
Question: 4: Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion?
- Antibiotic
- Analgesic
- Antacid
- Antiseptic
Answer: (c) Antacid
Explanation: Because of over eating our stomach produce more acid, which is generally resulting in indigestion. Thus, to neutralize excess acid produced by stomach antacid is taken as medicine. Thus answer is (c) Antacid
Question: 5: Write word equations and them balanced equations for the reaction taking place when
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules
Answer:
Sulphuric acid + Zn → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon
Answer:
Hydrochloric acid + Magnesium → Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder
Answer:
Sulphuric acid + Aluminium → Aluminium sulphate + Hydrogen
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron fillings.
Answer:
Hydrochloric acid + Fe → Iron chloride + Hydrogen
Question: 6: Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorized as acid. Describe an activity to prove it.
Answer:
A cork is taken and got fitted with two iron nails and connected to battery, bulb and switch.
Cork is placed in the beaker
Alcohol is poured in beaker in such a manner that half of the portion of nails is dipped in it.
Now switch is put on
Bulb is observed that whether it glows or not
This activity is repeated with glucose and hydrochloric acid solution
It is observed that bulb does not glow in the case of alcohol and glucose, but bulb glows in the case of hydrochloric acid solution.
Hydrogen ions are responsible for conduction of electricity in the case of acid. Since hydrochloric acid dissociates hydrogen ions in its aqueous solution, thus electricity conducts through the aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid. But aqueous solution of glucose and alcohol do not dissociate hydrogen ions in their aqueous solution, that’s why these solution do not conduct electricity and bulb does not glow.
This activity proves that alcohols and glucose are not acid instead they contain hydrogen because these do not dissociate hydrogen ions in their aqueous solution
NCERT Exercise solution:2
Question: 7: Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rain water does?
Answer: If an aqueous solution contains ions, then it conducts electricity otherwise not.
Since distilled water does not contain any salt and consequently does not conduct electricity. On the other hand rain water contains many salts as impurities. These salts dissociate ions in rain water because of which rain water conducts electricity.
This is the cause that distilled water does not conduct electricity whereas rain water conducts.
Question: 8: Why do acids not show acidic behavior in the absence of water?
Answer: An acid shows acidic behavior because of presence of hydrogen ions. Acid dissociates hydrogen ions only in their aqueous solution. This is the cause that acids do not show acidic behavior in the absence of water.
Question: 9: Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9 respectively. Which solution is
- Neutral?
- Strongly alkaline?
- Strongly acidic?
- Weakly acidic?
- Weakly alkaline?
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration.
Answer: Hydrogen ions concentration increases with decrease in pH value from 7 consequently strength of acid increases with decrease in pH value from 7 to 0.
On the other hand hydroxide ions concentration increases with increase in pH value from 7 consequently strength of acid increases with increase in pH value from 7 to 14.
While neutral solution has pH value equal to 7.
Therefore,
(a) Solution D is neutral having pH value equal to 7
(b) Solution C is strongly alkaline as its pH value is equal to 11
(c) Solution B is strongly acidic as its pH value is equal to 1
(d) Solution A is weakly acidic as its pH value is equal to 4
(e) Solution E is weakly alkaline as its pH value is equal to 9
Arrangement of given pH value in increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration:
11 < 9 < 7 < 4 < 1
Question: 10: Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. Amount and concentration taken for both acids are same. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Answer: Hydrochloric acid is stronger acid than acetic acid. Because of this, hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon more vigorously than acetic acid.
Thus, in test tube A in which hydrochloric acid is added with magnesium ribbon fizzing occurs more vigorously than test tube B in which acetic acid is added.
This happens because hydrochloric acid liberates hydrogen gas more vigorously than acetic acid.
Question: 11: Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Answer: Milk and curd both contains lactic acid. Curd has more concentration of lactic acid than milk.
Thus, when milk is turns into curd concentration of hydrogen ions increase since concentration of lactic acid increases. Thus, with increase in concentration of hydrogen ions pH value will decrease when milk turns into curd.
Question: 12: A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
- Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
- Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Answer: Milk starts curdling with increase in concentration of lactic acid produced by bacteria present in milk, i.e. curdling starts with decrease in pH value.
(a) Milkman shifts pH of fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline to delay the lactic acid produced by bacteria and hence milk takes more time to automatic curdling by adding a very small amount of baking soda.
(b) Acid present in milk is neutralized by adding of baking soda. That’s why this slightly alkaline milk takes long time to set as curd as production of acid takes more time.
Question: 13: Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture proof container. Explain why?
Answer: When plaster of Paris exposed to moisture present in air, it is converted into gypsum by absorbing water. This gypsum after some time starts drying and sets into hard mass.
This is the cause that Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture proof container to prevent it getting moisture from air.
Question: 14: What is the neutralization reaction? Give two examples.
Answer: Neutralization of an acid after reaction with a base is called neutralization reaction. In other words, when an acid reacts with a base, base neutralizes base after formation of water and respective salt, this is called neutralization reaction.
Example:
(a) When hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide (base), it produces sodium chloride and water because of neutralization reaction.
(b) When suplhuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide, sodium sulphate and water are formed after neutralization reaction.
Question: 15: Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda?
Answer:
Uses of washing soda:
(a) Used as detergent in cleaning of clothes
(b) Used to remove the permanent hardness of water
Uses of baking soda:
(a) In bakery to make batter soft
(b)Use as one of the material in fire extinguisher
class/std Ten Science
Acid, Base & Salt
NCERT Exemplar Solution:Short Answer1
Question: 31. Match the acids given in Column (A) with their correct source given
| Column(A) | Column(B) |
|---|---|
| (a) Lactic acid | (i) Toamto |
| (b) Acetic acid | (ii)Lemon |
| (c) Citric acid | (iii) Vinegar |
| (d) Oxalic acid | (iv) Curd |
Answer:
(a) – (iv)
(b) – (iii)
(c) – (ii)
(d) – (i)
Question: 32. Match the important chemicals given in Column (A) with the chemical formulae given in Column (B)
| Column(A) | Column(B) |
|---|---|
| (a) Plaster of Paris | (i) Ca(OH)2 |
| (b) Gypsum | (ii)CaSO4.1/2 H2O |
| (c) Bleaching Powser | (iii) CaSO4.2H2 |
| (d) Slaked Lime | (iv) CaOCl2 |
Answer:
(a) – (ii)
(b) – (iii)
(c) – (iv)
(d) – (i)
Question: 33. What will be the action of the following substances on litmus paper?
Dry HCl gas, Moistened NH3 gas, Lemon juice, Carbonated soft drink, Curd, Soap solution.
Answer:
Dry HCl: No action
Moistened NH3 gas: Turn blue litmus to red
Lemon Juice: Turn blue litmus to red
Carbonated soft drink: Turn blue litmus to red
Curd: Turn blue litmus to red
Soap solution: Turn red litmus to blue.
Question: 34. Name the acid present in ant sting and give its chemical formula. Also give the common method to get relief from the discomfort caused by the ant sting.
Answer:
Formic acid (methanoic acid) present in ant sting
Chemical Formula of formic acid: HCOOH
Common method to get relief from the discomfort caused by ant sting: Baking soda is rub over the place of ant stung which neutralizes the acid present in the sting and gives relief from discomfort.
Question: 35. What happens when nitric acid is added to egg shell?
Answer:
Egg shell contains mainly calcium carbonate.
Thus when nitric acid is added to egg shell, it forms carbon dioxide and calcium nitrate.
Question: 36. A student prepared solutions of (i) an acid and (ii) a base in two separate beakers. She forgot to label the solutions and litmus paper is not available in the laboratory. Since both the solutions are colourless, how will she distinguish between the two?
Answer:
It is assumed that other indicators will be available in laboratory. Thus, student will use other indicators, such as phenolphthalein.
Phenolphthalein turns pink with basic solution and remains colorless with acidic solution.
Thus, by using phenolphthalein, student can label the beakers (i) and (ii) having solution with acid and base.
Question: 37. How would you distinguish between baking powder and washing soda by heating?
Answer:
Baking powder (sodium hydrogen carbonate) produces carbon dioxide gas at very low temperature, while washing soda (sodium carbonate) does not produce carbon dioxide at low temperature, but washing soda produces carbon dioxide gas at very high temperature.
Thus, to distinguish between baking powder and washing soda, they are heated in separate test tubes.
Gases produced by them are passed through lime water.
Gas coming out from test tube which turns lime water milky is baking powder and which does not is washing soda.
NCERT Exemplar Solution:Short Answer2
Question: 38. Salt A commonly used in bakery products on heating gets converted into another salt B which itself is used for removal of hardness of water and a gas C is evolved. The gas C when passed through lime water, turns it milky. Identify A, B and C.
Answer: When baking powder is heated, it produces carbon dioxide, water and sodium carbonate. Sodium carbonate is used for removal of hardness of water.
Therefore, given salt A is baking powder (sodium hydrogen carbonate) which is used in bakery products to make batter soft.
Salt B is sodium carbonate. This is used for removal of hardness of water.
Gas C is carbon dioxide, which when passes through lime water, lime water turns milky.
Question: 39. In one of the industrial processes used for manufacture of sodium hydroxide, a gas X is formed as by product. The gas X reacts with lime water to give a compound Y which is used as a bleaching agent in chemical industry. Identify X and Y giving the chemical equation of the reactions involved.
Answer:
In Solvay process, this is an Industrial process, used for manufacture of sodium hydroxide from brine (aqueous solution of sodium chloride).
When electric current is passed through brine, chlorine gas and hydrogen gases are formed along with sodium hydroxide.
One of the bi-products in this process is chlorine. When chlorine reacts with lime water (calcium hydroxide), calcium oxychloride (bleaching powder) is formed.
This bleaching powder is used as a bleaching agent in chemical industry.
Thus,
Gas ‘X’ is chlorine
Compound ‘Y’ is calcium oxychloride (bleaching powder)
Question: 40. Fill in the missing data in the following table
| Name of salt | Formula | Salt obtained from | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | Acid | ||
| (i)Ammonium chloride | NH4Cl | NH4OH | — |
| (ii)Copper sulphate | — | — | H2SO4 |
| (iii)Sodium chloride | NaCl | NaOH | — |
| (iv)Magnesium nitrate | Mg(NO3 )2 | — | HNO3 |
| (v)Potassium sulphate | K2SO4 | — | — |
| (vi)Calcium nitrate | Ca(NO3 )2 | Ca(OH)2 | — |
Answer:
| Name of salt | Formula | Salt obtained from | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | Acid | ||
| (i)Ammonium chloride | NH4Cl | NH4OH | HCl |
| (ii)Copper sulphate | CuSO4 | Cu(OH)2 | H2SO4 |
| (iii)Sodium chloride | NaCl | NaOH | HCl |
| (iv)Magnesium nitrate | Mg(NO3 )2 | Mg(OH)2 | HNO3 |
| (v)Potassium sulphate | K2SO4 | KOH | H2SO4 |
| (vi)Calcium nitrate | Ca(NO3 )2 | Ca(OH)2 | HNO3 |
Question: 41. What are strong and weak acids? In the following list of acids, separate strong acids from weak acids.
Hydrochloric acid, citric acid, acetic acid, nitric acid, formic acid, sulphuric acid.
Answer:
Strong Acid: Acids that ionize completely in their aqueous solution are called strong acids. Most of the mineral acids are strong.
Weak Acid: Acids that do not ionize completely in their aqueous solution are called weak acids. Most of the organic acids are weak.
Hydrochloric acid, Nitric Acid, Sulphuric Acid: Strong Acid
Citric Acid, Acetic Acid, Formic Acid: Weak Acid
Question: 42. When zinc metal is treated with a dilute solution of a strong acid, a gas is evolved, which is utilized in the hydrogenation of oil. Name the gas evolved. Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved and also write a test to detect the gas formed.
Answer: When zinc metal is treated with dilute solution of sulphuric acid or other strong acids, zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas are formed.
Hydrogen gas is utilized in hydrogenation of oil.
Hydrogen gas burns with pop sound. Thus when a burning candle is brought near the gas evolved, if it burns with pop sound, this confirms the presence of hydrogen gas.
NCERT Exemplar Solution:Long Answer
Question: 43. In the following schematic diagram for the preparation of hydrogen gas as shown in Figure 2.3, what would happen if following changes are made?
(a) In place of zinc granules, same amount of zinc dust is taken in the test tube
(b) Instead of dilute sulphuric acid, dilute hydrochloric acid is taken
(c) In place of zinc, copper turnings are taken
(d) Sodium hydroxide is taken in place of dilute sulphuric acid and the tube is heated.
Answer:
(a) In the case of zinc dust instead of zinc granules, hydrogen gas is formed.
When zinc dust reacts with sulphuric acid hydrogen gas and zinc sulphate are formed.
(b) If dilute hydrochloric acid is taken instead of sulphuric acid same result will form, i.e. hydrogen gas evolves.
When zinc granules react with dilute hydrochloric acid, it gives zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
(c) If copper turning are taken at the place of zinc granules, in this case also hydrogen gas is formed.
When copper turning reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, copper sulphate and hydrogen gas are formed.
(d) If sodium hydroxide is taken in place of dilute sulphuric acid and the tube is heated, in this case also hydrogen gas is formed.
When zinc is heated with sodium hydroxide, sodium zincate and hydrogen gas are formed.
Question: 44. For making cake, baking powder is taken. If at home your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder in cake,
(a) how will it affect the taste of the cake and why?
(b) how can baking soda be converted into baking powder?
(c) what is the role of tartaric acid added to baking soda?
Answer:
(a) When baking soda is heated, it gives carbon dioxide, water and sodium carbonate.
Thus, if baking soda is used in making of cake, formation of sodium carbonate makes the taste of cake bitter. Because sodium carbonate is a base and a base is bitter in taste.
On the other hand, baking powder on heating does not forms sodium carbonate, and hence does not make the taste of cake bitter.
(b) Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and tartaric acid or other edible acid.
Baking powder is made by mixing of baking soda and tartaric acid or other mild edible acid.
(c) There are two roles of baking powder in making of cake:
(i) When water is added to the baking powder, tartaric acid present in baking powder dissociates hydrogen ions. These hydrogen ions react with sodium bicarbonate and produce carbon dioxide at room temperature. Carbon dioxides get trapped into dough and come out very slowly in the form of bubbles. These bubbles make the batter of cake soft and spongy.
(ii) On heating of baking powder, sodium carbonate also formed. This sodium carbonate reacts with acid present in baking powder and produces sodium tartarate and water.
Taste and smell of sodium tartarate is pleasant. This gives pleasant smell and taste to cake.
Question: 45. A metal carbonate X on reacting with an acid gives a gas which when passed through a solution Y gives the carbonate back.
On the other hand, a gas G that is obtained at anode during electrolysis of brine is passed on dry Y, it gives a compound Z, used for disinfecting drinking water. Identity X, Y, G and Z.
Answer:
Part (A)
When calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide gas, water and calcium chloride are formed.
When the carbon dioxide is passed through the lime water, lime water turns milky because of the formation of calcium carbonate.
Therefore,
Metal carbonate ‘X’ is calcium carbonate.
Solution ‘Y’ is lime water (Calcium hydroxide).
Part (B)
When electric current is passed through brine (solution of sodium chloride), chlorine gas is deposited near anode. When chlorine gas is passed over dry slaked lime (calcium hydroxide), it produces calcium oxychloride (bleaching powder) and with water.
The bleaching powder (calcium oxychloride) is used for disinfecting of drinking water.
Thereore,
Gas ‘G’ is chlorine gas.
Dry ‘Y’ is dry calcium hydroxide (dry slaked lime).
Compound ‘Z‘ is bleaching powder (Calcium oxychloride).
NCERT Exemplar Solution:Long Answer2
Question: 46. A dry pellet of a common base B, when kept in open absorbs moisture and turns sticky. The compound is also a byᾰproduct of chlor—alkali process. Identify B. What type of reaction occurs when B is treated with an acidic oxide? Write a balanced chemical equation for one such solution.
Answer:
(Part—A)
Dry pellets of sodium hydroxide absorb moisture and turn sticky when kept in open. Sodium hydroxide is a byproduct of chlor—alkali process.
Therefore, common base ‘B’ is sodium hydroxide.
(Part—B)
Non-metallic oxides are also known as acidic oxide. For example: carbon dioxide.
Acidic oxides give salt and water when reacts with a base.
Example:
When sodium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide (acidic oxide), sodium carbonate and water are formed.
Question: 47. A sulphate salt of Group 2 element of the Periodic Table is a white, soft substance, which can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough. When this compound is left in open for some time, it becomes a solid mass and cannot be used for moulding purposes. Identify the sulphate salt and why does it show such a behaviour? Give the reaction involved.
Answer:
Calcium is a Group 2 element in Periodic Table.
Sulphate salt of calcium is calcium sulphate. The common name of calcium sulphate hemihydrate is Plaster of Paris. The chemical formula is CaSO 4. ½ H2O.
Plaster of Paris is a white soft substance and is used in moulding of clay, toys, desining of wall, etc. after making its dough.
When Plaster of Paris is left in open for some times, it gets hydrated, and turns into Gypsum. The chemical formula of Gypsum is CaSO 4. 2 H2O. This Gypsum again dehydrated after some times and turns into solid mass. After turning into solid mass it cannot be used for moulding purpose.
Calcium belongs to group 2 in periodic table, and it’s sulphate salt is Plaster of Paris.
Question: 48. Identify the compound X on the basis of the reactions given below. Also, write the name and chemical formulae of A, B and C.
Answer:
Therefore,
Compound ‘X’ is sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Compound ‘A’ is Zinc sulpahte (ZnSO4)
Compound ‘B’ is Sodium chloride (NaCl).
Compound ‘C’ is sodium acetate (CH3COONa)


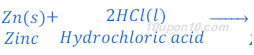
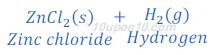
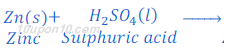
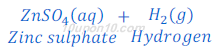

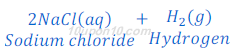

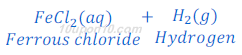
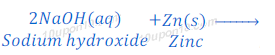
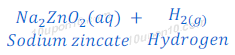
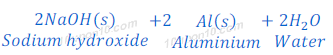
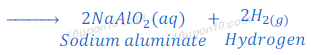
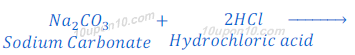
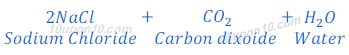
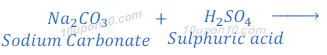
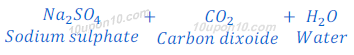


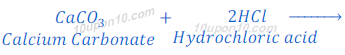
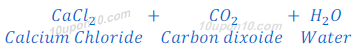
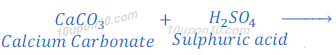
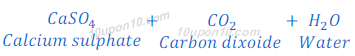
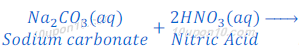
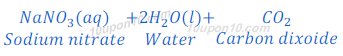
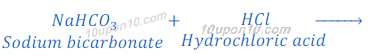

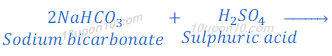
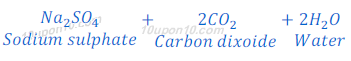
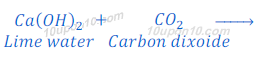
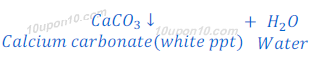
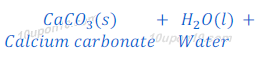

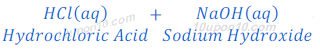
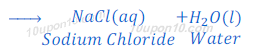
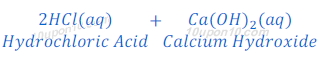
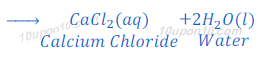
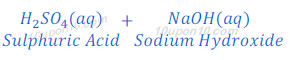
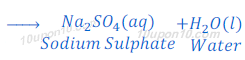
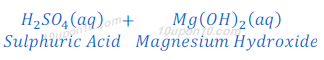
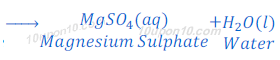
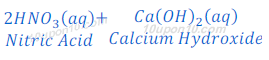
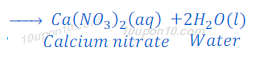
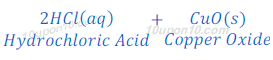
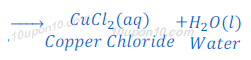
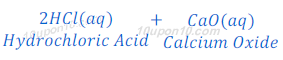
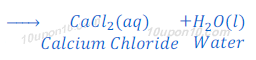
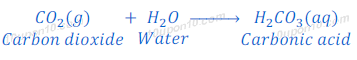
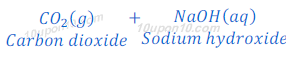
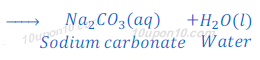
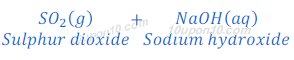
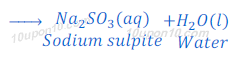
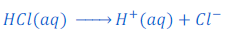
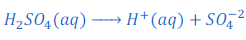

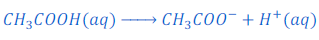
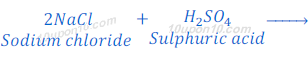
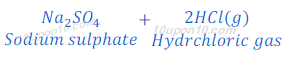

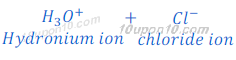
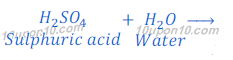
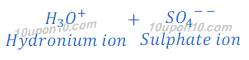
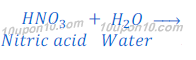
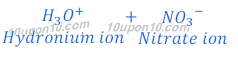
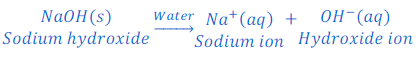
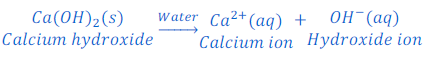
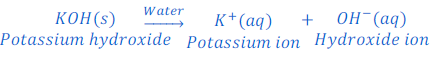
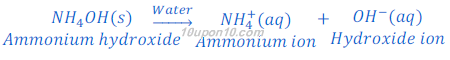
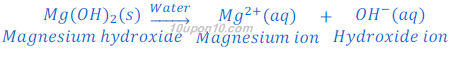
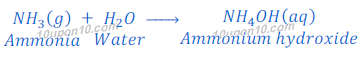
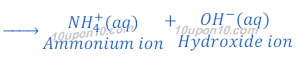

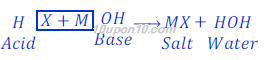
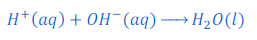

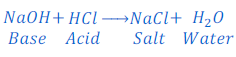
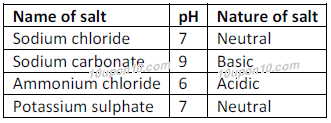
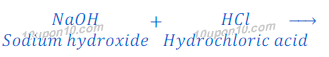

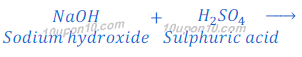
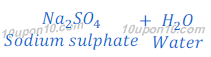

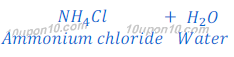
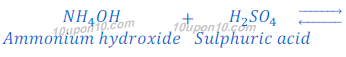
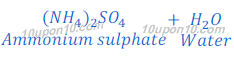
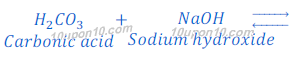
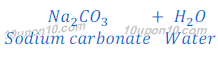

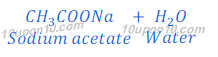
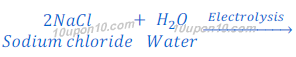
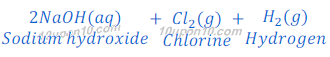
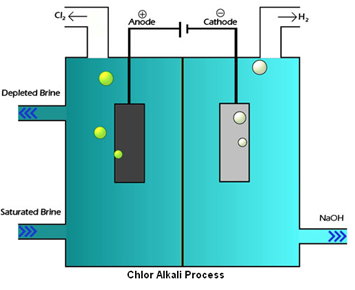
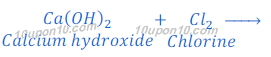
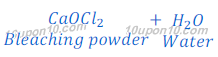
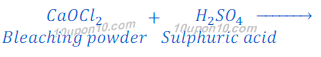
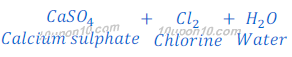
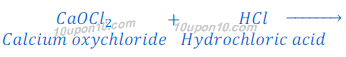
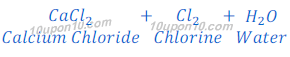
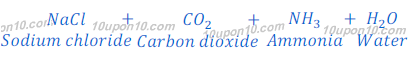

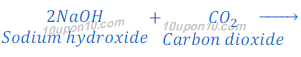
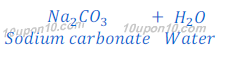
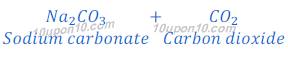
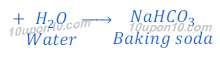

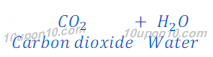
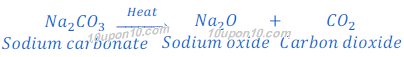
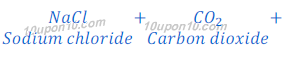
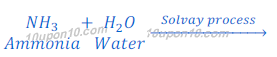
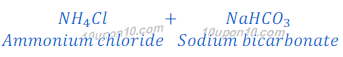

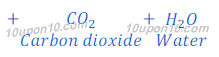



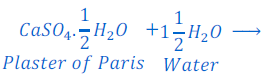
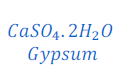
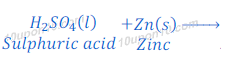
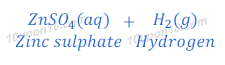
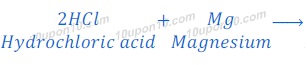


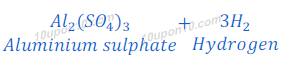
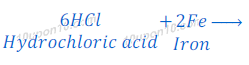
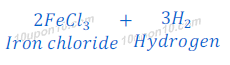

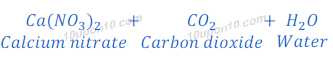
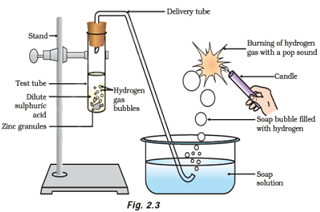
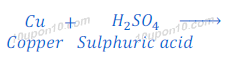
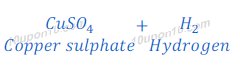
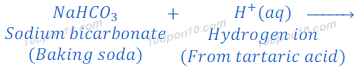
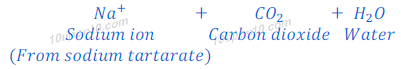
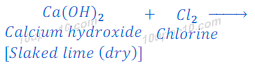
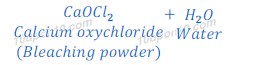
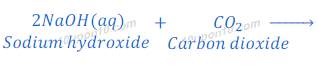
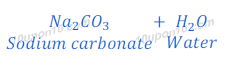
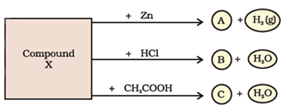

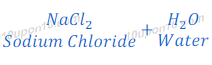
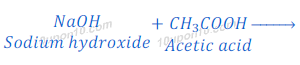
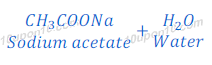










Nice sir
ReplyDelete